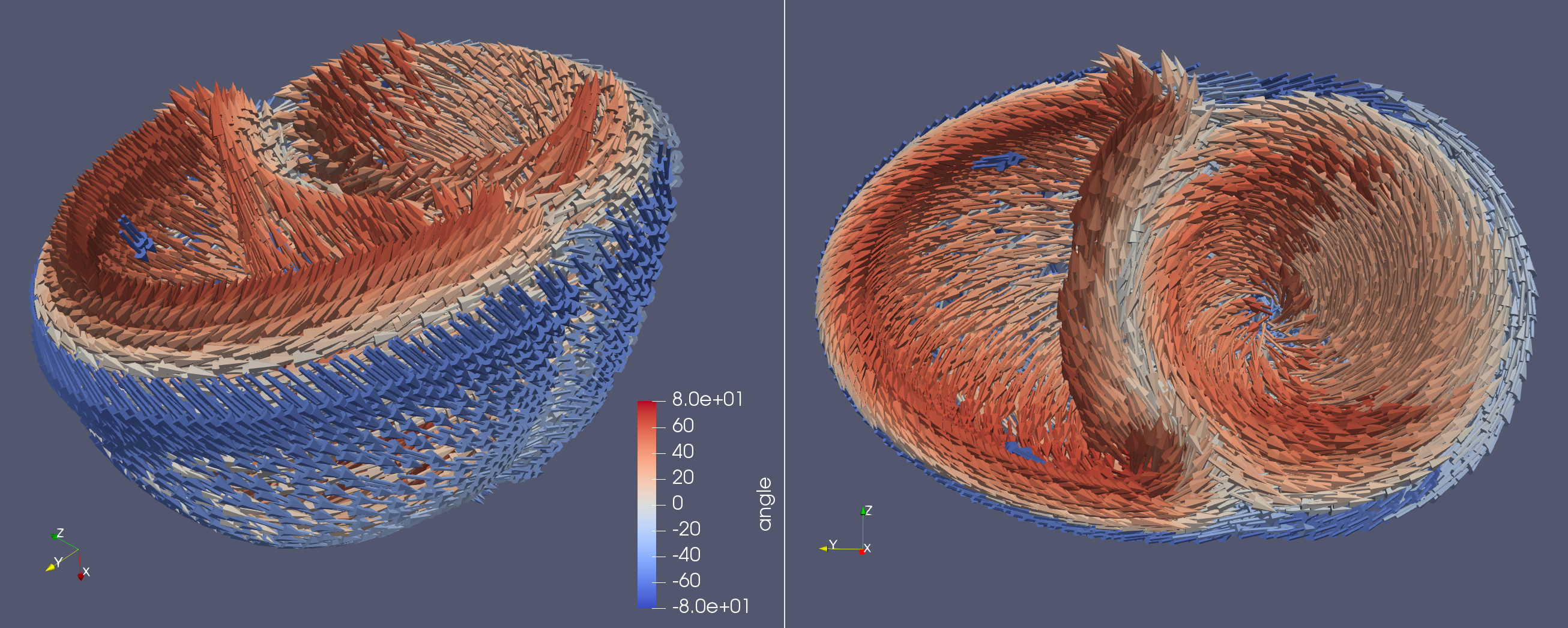
Creating fibers on a simple BiV ellipsoid
Creating fibers on a simple BiV ellipsoid¶
In this demo we create a simple BiV ellipsoid using mshr.
You can install mshr using conda. It also possible to create ellipsoidal geometries using gmsh, see e.g https://github.com/finsberg/pulse/blob/0d7b5995f62f41df4eec9f5df761fa03da725f69/pulse/geometries.py#L160
import dolfin as df
import ldrb
# Here we just create a lv mesh. Here you can use yor own mesh instead.
geometry = ldrb.create_biv_mesh()
# The mesh
mesh = geometry.mesh
# The facet function (function with marking for the boundaries)
ffun = geometry.ffun
# A dictionary with keys and values for the markers
markers = geometry.markers
# Also if you want to to this demo in parallell you should create the mesh
# in serial and save it to e.g xml
# df.File('lv_mesh.xml') << mesh
# or xdmf
with df.XDMFFile(mesh.mpi_comm(), "mesh.xdmf") as xdmf:
xdmf.write(mesh)
# And when you run the code in paralall you should load the mesh from the file.
# mesh = df.Mesh('lv_mesh.xml')
# or with xdmf
mesh = df.Mesh()
with df.XDMFFile("mesh.xdmf") as xdmf:
xdmf.read(mesh)
# You should also save the facet function
with df.XDMFFile(mesh.mpi_comm(), "ffun.xdmf") as xdmf:
xdmf.write(ffun)
# and read it agin
ffun = df.MeshFunction("size_t", mesh, 2)
with df.XDMFFile("ffun.xdmf") as xdmf:
xdmf.read(ffun)
# Choose space for the fiber fields
# This is a string on the form {family}_{degree}
fiber_space = "Lagrange_2"
# Compute the microstructure
fiber, sheet, sheet_normal = ldrb.dolfin_ldrb(
mesh=mesh,
fiber_space=fiber_space,
ffun=ffun,
markers=markers,
alpha_endo_lv=30, # Fiber angle on the LV endocardium
alpha_epi_lv=-30, # Fiber angle on the LV epicardium
beta_endo_lv=0, # Sheet angle on the LV endocardium
beta_epi_lv=0, # Sheet angle on the LV epicardium
alpha_endo_sept=60, # Fiber angle on the Septum endocardium
alpha_epi_sept=-60, # Fiber angle on the Septum epicardium
beta_endo_sept=0, # Sheet angle on the Septum endocardium
beta_epi_sept=0, # Sheet angle on the Septum epicardium
alpha_endo_rv=80, # Fiber angle on the RV endocardium
alpha_epi_rv=-80, # Fiber angle on the RV epicardium
beta_endo_rv=0, # Sheet angle on the RV endocardium
beta_epi_rv=0,
)
# Store the results
with df.HDF5File(mesh.mpi_comm(), "biv.h5", "w") as h5file:
h5file.write(fiber, "/fiber")
h5file.write(sheet, "/sheet")
h5file.write(sheet_normal, "/sheet_normal")
If you run in parallel you should skip the visualisation step and do that in serial in stead. In that case you can read the the functions from the xml Using the following code
V = ldrb.space_from_string(fiber_space, mesh, dim=3)
fiber = df.Function(V)
sheet = df.Function(V)
sheet_normal = df.Function(V)
with df.HDF5File(mesh.mpi_comm(), "biv.h5", "r") as h5file:
h5file.read(fiber, "/fiber")
h5file.read(sheet, "/sheet")
h5file.read(sheet_normal, "/sheet_normal")
You can also store files in XDMF which will also compute the fiber angle as scalars on the glyph to be visualised in Paraview. Note that these functions don’t work (yet) using mpirun
# (These function are not tested in parallel)
ldrb.fiber_to_xdmf(fiber, "biv_fiber")
# ldrb.fiber_to_xdmf(sheet, "biv_sheet")
# ldrb.fiber_to_xdmf(sheet_normal, "biv_sheet_normal")