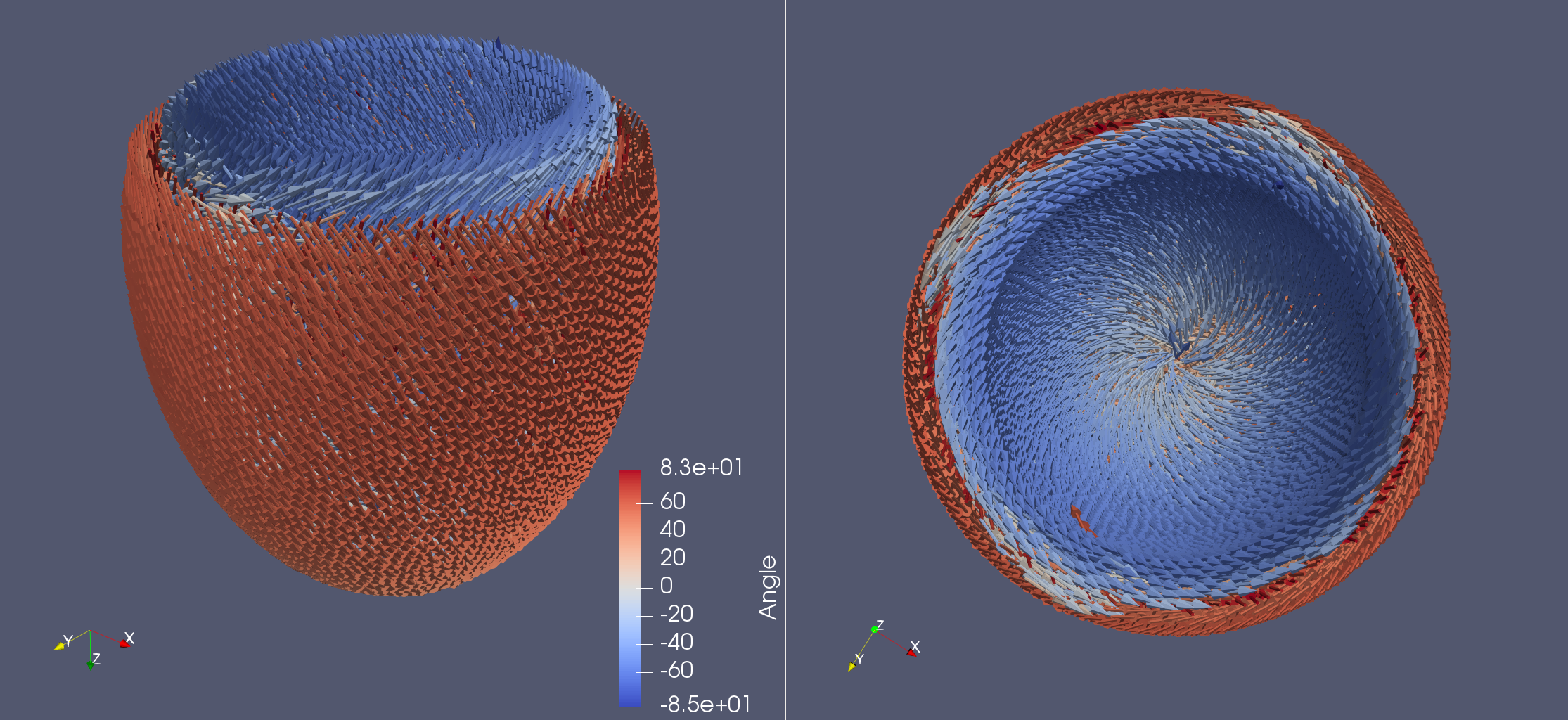
Life X - idealized_LV
Life X - idealized_LV¶
Life X recently published their own implementation of the LDRB algorithm and with that they also publushed a lot of example meshes. This demo aims to try out this implementation of the LDRB algorithm on these example meshes. The LifeX example meshes can be found at https://zenodo.org/record/5810269#.YeEjWi8w1B0, which also contains a DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5810269.
This demo assumes that you have downloaded the folder with the meshes in the same format as they are uploaded on zenodo, so that the gmsh files are located in a folder called lifex_fiber_generation_examples/mesh.
First we import the necessary packages. Note that we also import meshio which is used for converted from .msh (gmsh) to .xdmf (FEnICS).
import dolfin
import ldrb
Load the mesh and markers.
mesh, ffun, markers = ldrb.gmsh2dolfin(
"lifex_fiber_generation_examples/mesh/idealized_LV.msh",
)
Here the markers are actually parsed with meshio, but they have the wrong name so we just rename them
ldrb_markers = {
"epi": markers["Epicardium"][0],
"lv": markers["Endocardium"][0],
"base": markers["Basal plane"][0],
}
Select linear langange elements
fiber_space = "P_1"
Compute the fiber-sheet system
fiber, sheet, sheet_normal = ldrb.dolfin_ldrb(
mesh=mesh,
fiber_space=fiber_space,
ffun=ffun,
markers=ldrb_markers,
alpha_endo_lv=60, # Fiber angle on the endocardium
alpha_epi_lv=-60, # Fiber angle on the epicardium
beta_endo_lv=0, # Sheet angle on the endocardium
beta_epi_lv=0, # Sheet angle on the epicardium
)
And save the results
with dolfin.XDMFFile(mesh.mpi_comm(), "idealized_LV_fiber.xdmf") as xdmf:
xdmf.write(fiber)