Optimizing Parameters for Healthy Baseline#
This script demonstrates how to tune the Regazzoni2020 circulation model to match
specific hemodynamic targets representing a physiologically healthy adult.
The Goal: Clinical Targets vs. Model Parameters#
Before running an optimization, it is crucial to understand the gap between what we want to achieve (Clinical Targets) and what we can actually control in the code (Model Parameters).
Clinical Targets (What we want)#
These are the emergent properties measured in a clinic. We want our digital twin to match these values:
Systemic Blood Pressure: ~120/80 mmHg.
Stroke Volume (SV): ~70 mL.
Ejection Fraction (EF): ~50-60%.
Right Ventricle Pressure: ~25/4 mmHg.
Model Parameters (What we have)#
The Regazzoni2020 model does not have a “Set Blood Pressure” button. Instead, it is governed by physical constants that describe the heart and vessels (Contractility, Stiffness, Resistance, Compliance).
The Challenge#
Tuning a closed-loop circulation model is difficult because everything is coupled. Changing systemic resistance affects LV pressure, which affects RV filling, and so on. Furthermore, Preload is tricky because you cannot simply “set” the End-Diastolic Pressure (EDP); it is an emergent property of the total blood volume and venous compliance.
The Solution#
To address these challenges, we employ a numerical optimizer (scipy.optimize) alongside two critical strategies to ensure robust convergence.
First, we implement Parameter Scaling to normalize all inputs to a magnitude of approximately ~1.0. Second, we require Volume Offset Control, creating a synthetic parameter called TOTAL_VOLUME_OFFSET to allow high-level control of ventricular preload.
Define Targets#
These are the physiological values we want the model to reproduce.
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.optimize import minimize, Bounds
from circulation.regazzoni2020 import Regazzoni2020
import logging
# Define Targets
targets = {
"LV_ESP": 120.0, # Left Ventricle End-Systolic Pressure [mmHg]
"LV_EDP": 10.0, # Left Ventricle End-Diastolic Pressure [mmHg]
"SV": 70.0, # Stroke Volume [mL]
"RV_ESP": 25.0, # Right Ventricle End-Systolic Pressure [mmHg]
"RV_EDP": 4.0, # Right Ventricle End-Diastolic Pressure [mmHg]
"Ao_DBP": 80.0, # Aortic Diastolic Blood Pressure [mmHg]
}
print("Target Hemodynamics:")
for key, value in targets.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
Target Hemodynamics:
LV_ESP: 120.0
LV_EDP: 10.0
SV: 70.0
RV_ESP: 25.0
RV_EDP: 4.0
Ao_DBP: 80.0
The “Model Interface” Helper#
This class handles the “magic” of translating between the Optimizer (which likes simple, scaled numbers) and the Physics Model (which needs real physical units and complex initialization).
Key Concept: Volume Offset
To change Preload (filling pressure), we must alter the total blood volume. This relies on the relationship \(V = C \cdot P\). By modifying the initial condition p_VEN_SYS (Systemic Venous Pressure), we adjust the pressure in the large systemic venous capacitor.
class ModelInterface:
def __init__(self):
# Initialize a base model to get default structures
self.base_model = Regazzoni2020(add_units=False)
logging.getLogger('circulation.base').setLevel(logging.WARNING)
self.base_params = self.base_model.parameters
self.base_init = self.base_model._initial_state
# Configuration: (Parameter Name, Initial Guess, Lower Bound, Upper Bound, Scale Factor)
# Scale Factor is used to divide the real value so the optimizer sees ~1.0
self.config = [
# Contractility (EA) - Represents E_max (End-Systolic Elastance).
# "Strength" of the pump. Higher EA -> Higher Systolic Pressure.
("chambers.LV.EA", 3.5, 1.0, 10.0, 1.0),
("chambers.RV.EA", 0.6, 0.2, 5.0, 1.0),
# Passive Stiffness (EB) - Represents passive stiffness during diastole.
# Affects how easily the ventricle fills (Preload).
("chambers.LV.EB", 0.1, 0.01, 1.0, 0.1),
("chambers.RV.EB", 0.05, 0.01, 1.0, 0.1),
# Resistance (R) - Opposition to blood flow.
("circulation.SYS.R_AR", 1.05, 0.5, 3.0, 1.0), # Systemic Resistance
("circulation.PUL.R_AR", 0.08, 0.01, 1.0, 1.0), # Pulmonary Resistance
# Compliance (C) - Elasticity of arteries and veins.
("circulation.SYS.C_AR", 1.1, 0.5, 3.0, 1.0), # Arterial Compliance
("circulation.SYS.C_VEN", 50.0, 10.0, 150.0, 10.0), # Venous Compliance (Reservoir)
# VOLUME OFFSET CONTROL (Synthetic Parameter)
# We allow the optimizer to add/remove up to 500mL of blood
("TOTAL_VOLUME_OFFSET", 0.0, -500.0, 500.0, 100.0)
]
def get_initial_guess(self):
"""Returns scaled initial parameters for the optimizer."""
return [val/scale for _, val, _, _, scale in self.config]
def get_bounds(self):
"""Returns scaled bounds for the optimizer."""
return [(lb/scale, ub/scale) for _, _, lb, ub, scale in self.config]
def update_model(self, scaled_x):
"""
Converts scaled optimizer variables back to physical model parameters.
"""
params = self.base_params.copy()
init_state = self.base_init.copy()
for val, (key, _, _, _, scale) in zip(scaled_x, self.config):
real_val = val * scale
if key == "TOTAL_VOLUME_OFFSET":
# Adjusting p_VEN_SYS changes the total volume in the system.
# Delta_P = Delta_V / C_ven
C_ven = params["circulation"]["SYS"]["C_VEN"]
# Get current venous pressure
current_p = init_state["p_VEN_SYS"]
if hasattr(current_p, "magnitude"): current_p = current_p.magnitude
# Apply the offset
init_state["p_VEN_SYS"] = current_p + (real_val / C_ven)
else:
# Standard parameter update (navigate nested dict)
keys = key.split(".")
d = params
for k in keys[:-1]:
d = d[k]
d[keys[-1]] = real_val
return params, init_state
The Cost Function#
This function runs the simulation and calculates a “score” (Cost). Lower cost means the simulation matches the targets better.
Note on Weights: We assign different weights to different errors.
High Weight (SV): Stroke Volume is the most important output.
Barrier Penalty (Ao_DBP): If blood pressure drops too low (< 70), the model can become unstable. We add a huge penalty to force the optimizer away from these “crash” regions.
interface = ModelInterface()
iteration_counter = [0] # Mutable counter
def cost_function(scaled_x):
# Decode parameters
params, init_state = interface.update_model(scaled_x)
# Run Simulation
model = Regazzoni2020(parameters=params, initial_state=init_state, add_units=False, verbose=False)
logging.getLogger('circulation.base').setLevel(logging.WARNING)
try:
# Run 10 beats to reach steady state
history = model.solve(num_beats=10, dt=2e-3)
except (RuntimeError, ValueError):
# If simulation crashes, return huge cost
return 1e6
# Extract Metrics from Last Beat
samples = int((1/params["HR"]) / 2e-3)
slc = slice(-samples, None)
p_lv = history["p_LV"][slc]
v_lv = history["V_LV"][slc]
p_rv = history["p_RV"][slc]
v_rv = history["V_RV"][slc]
p_ao = history["p_AR_SYS"][slc]
if np.max(p_rv) > 300.0 or np.isnan(np.sum(p_rv)):
#safety check for unphysiological from PH optimization
return 1e6
metrics = {
"LV_ESP": np.max(p_lv),
"LV_EDP": np.min(p_lv),
"SV": np.max(v_lv) - np.min(v_lv),
"RV_ESP": np.max(p_rv),
"RV_EDP": np.min(p_rv),
"Ao_DBP": np.min(p_ao)
}
# Calculate Weighted Error
cost = 0.0
# Primary Target: Stroke Volume
cost += 50.0 * ((metrics["SV"] - targets["SV"]) / targets["SV"])**2
# Balance: RV Output should match LV Output
rv_sv = np.max(v_rv) - np.min(v_rv)
cost += 20.0 * ((metrics["SV"] - rv_sv) / targets["SV"])**2
# LV Pressures
cost += 10.0 * ((metrics["LV_ESP"] - targets["LV_ESP"]) / targets["LV_ESP"])**2
cost += 10.0 * ((metrics["LV_EDP"] - targets["LV_EDP"]) / targets["LV_EDP"])**2
# RV Pressures (Increased weight for precision)
cost += 5.0 * ((metrics["RV_ESP"] - targets["RV_ESP"]) / targets["RV_ESP"])**2
cost += 5.0 * ((metrics["RV_EDP"] - targets["RV_EDP"]) / targets["RV_EDP"])**2
# Safety Barrier: Aortic Pressure
if metrics["Ao_DBP"] < 60.0:
# Huge penalty if pressure drops unphysiologically low
cost += 100.0 * ((60.0 - metrics["Ao_DBP"]) / 60.0)**2
else:
cost += 50.0 * ((metrics["Ao_DBP"] - targets["Ao_DBP"]) / targets["Ao_DBP"])**2
# Logging
if iteration_counter[0] % 10 == 0:
print(f"Iter {iteration_counter[0]:3d} | Cost: {cost:.4f} | SV: {metrics['SV']:.1f} mL")
print(f" LV: {metrics['LV_ESP']:.0f}/{metrics['LV_EDP']:.0f} | "
f"RV: {metrics['RV_ESP']:.0f}/{metrics['RV_EDP']:.0f} | "
f"Ao: {metrics['Ao_DBP']:.0f}")
iteration_counter[0] += 1
return cost
Run Optimization#
We use the Nelder-Mead algorithm, which is robust for non-smooth problems like this.
print("\nStarting Optimization...")
x0 = interface.get_initial_guess()
bounds = interface.get_bounds()
# Reset counter
iteration_counter[0] = 0
maxiter = 20 if os.getenv("CI") else 1000 # Limit iterations for CI environments
result = minimize(
cost_function,
x0,
method='Nelder-Mead',
bounds=Bounds([b[0] for b in bounds], [b[1] for b in bounds]),
options={'maxiter': maxiter, 'xatol': 1e-4, 'fatol': 1e-4, 'disp': True}
)
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("Optimization Complete!")
print("="*60)
Starting Optimization...
Iter 0 | Cost: 8.8527 | SV: 75.0 mL
LV: 163/7 | RV: 26/4 | Ao: 109
Iter 10 | Cost: 6.8786 | SV: 75.3 mL
LV: 158/7 | RV: 27/4 | Ao: 105
Iter 20 | Cost: 4.2043 | SV: 74.5 mL
LV: 153/8 | RV: 27/4 | Ao: 98
Iter 30 | Cost: 1.1760 | SV: 74.3 mL
LV: 139/8 | RV: 27/4 | Ao: 84
============================================================
Optimization Complete!
============================================================
/tmp/ipykernel_2219/4009544868.py:8: RuntimeWarning: Maximum number of iterations has been exceeded.
result = minimize(
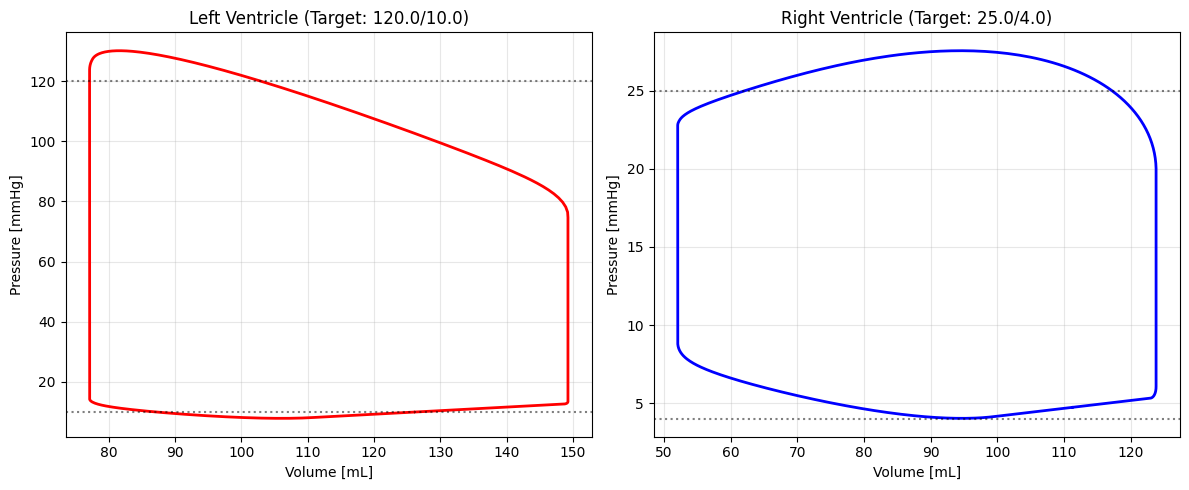
Analyze Results#
Let’s look at the final parameters and run a verification simulation.
final_params, final_init = interface.update_model(result.x)
print("Final Optimized Parameters:")
for i, (key, _, _, _, scale) in enumerate(interface.config):
val = result.x[i] * scale
unit = "mL" if "OFFSET" in key else ""
print(f" {key:<25}: {val:.3f} {unit}")
print(f"\nFinal Cost: {result.fun:.6f}")
# Verification Run
print("\nRunning Verification Simulation...")
model_opt = Regazzoni2020(parameters=final_params, initial_state=final_init, add_units=False)
history = model_opt.solve(num_beats=20, dt=1e-3)
# Plotting
samples = int((1/final_params["HR"]) / 1e-3)
slc = slice(-samples, None)
p_lv = history["p_LV"][slc]
v_lv = history["V_LV"][slc]
p_rv = history["p_RV"][slc]
v_rv = history["V_RV"][slc]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
# LV Loop
axs[0].plot(v_lv, p_lv, 'r-', lw=2, label="Optimized")
axs[0].set_title(f"Left Ventricle (Target: {targets['LV_ESP']}/{targets['LV_EDP']})")
axs[0].set_xlabel("Volume [mL]")
axs[0].set_ylabel("Pressure [mmHg]")
axs[0].axhline(targets['LV_ESP'], color='k', ls=':', alpha=0.5)
axs[0].axhline(targets['LV_EDP'], color='k', ls=':', alpha=0.5)
axs[0].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# RV Loop
axs[1].plot(v_rv, p_rv, 'b-', lw=2, label="Optimized")
axs[1].set_title(f"Right Ventricle (Target: {targets['RV_ESP']}/{targets['RV_EDP']})")
axs[1].set_xlabel("Volume [mL]")
axs[1].set_ylabel("Pressure [mmHg]")
axs[1].axhline(targets['RV_ESP'], color='k', ls=':', alpha=0.5)
axs[1].axhline(targets['RV_EDP'], color='k', ls=':', alpha=0.5)
axs[1].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Final Optimized Parameters:
chambers.LV.EA : 3.465
chambers.RV.EA : 0.586
chambers.LV.EB : 0.118
chambers.RV.EB : 0.050
circulation.SYS.R_AR : 0.723
circulation.PUL.R_AR : 0.092
circulation.SYS.C_AR : 1.020
circulation.SYS.C_VEN : 53.853
TOTAL_VOLUME_OFFSET : 0.017 mL
Final Cost: 0.825708
Running Verification Simulation...