Lorentz Attractor#
In this demo we solve the Lorentz attractor
with the parameters \(\sigma=10.0, \rho=28.0\) and \(beta=8/3\) and the initial conditions \(x = 0.0, y = 1.0\), and \(z = 1.05\).
We assume that the we have file called lorentz.ode with the following content
# lorentz.ode
parameters(
sigma=12.0,
rho=21.0,
beta=2.4
)
states(
x=1.0,
y=2.0,
z=3.05
)
dx_dt = sigma * (y - x)
dy_dt = x * (rho - z) - y
dz_dt = x * y - beta * z
And we note that the parameters and initial states are not the same as stated about, so we need to somehow provide the correct parameters and initial states.
First let’s do the usual imports
import goss
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from gotran import load_ode
And load the ode using gotran
lorentz = load_ode("lorentz.ode")
Next we jit-compile the ODE into goss
ode = goss.ParameterizedODE(lorentz)
We can update the parameters using the set_parameter method
ode.set_parameter("sigma", 10.0)
ode.set_parameter("rho", 28.0)
ode.set_parameter("beta", 8 / 3)
We can now instantiate the solver and select the time steps
solver = goss.solvers.RKF32(ode)
t = np.linspace(0, 100, 10001)
We can also provide the correct initial states to the solver
ic = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 1.05])
u = solver.solve(t, y0=ic)
Finally we plot the solution
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection="3d")
ax.plot(u[:, 0], u[:, 1], u[:, 2], lw=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("X Axis")
ax.set_ylabel("Y Axis")
ax.set_zlabel("Z Axis")
ax.set_title("Lorenz Attractor")
plt.show()
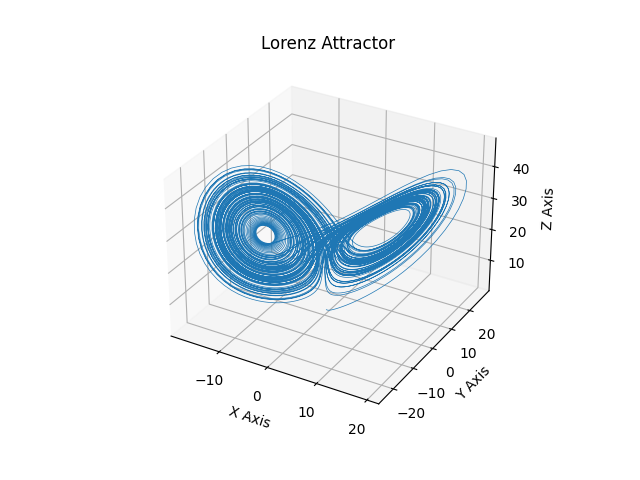
Fig. 1 Computed solution of the lorentz attractor#
